- +919659859896
- india@mrg-composites.com
- We Ship Worldwide
- Download Company Profile
ISO 9001:2015 Certified
What’s GFRP Rebar?
Here’s Why It’s a Game-Changer for Foundation
Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer – GFRP rebar is a cutting-edge building material. GFRP Rebar is rapidly gaining popularity in construction. It consists of glass fibers and a polymer resin. GFRP rebar is non-corrosive, lightweight, and stronger than traditional steel rebar. Its durability makes it an excellent choice for foundation construction, especially in environments where corrosion is a concern. GFRP rebar reduces long-term maintenance costs, making it a sustainable and cost-effective solution for home building and large construction projects alike.
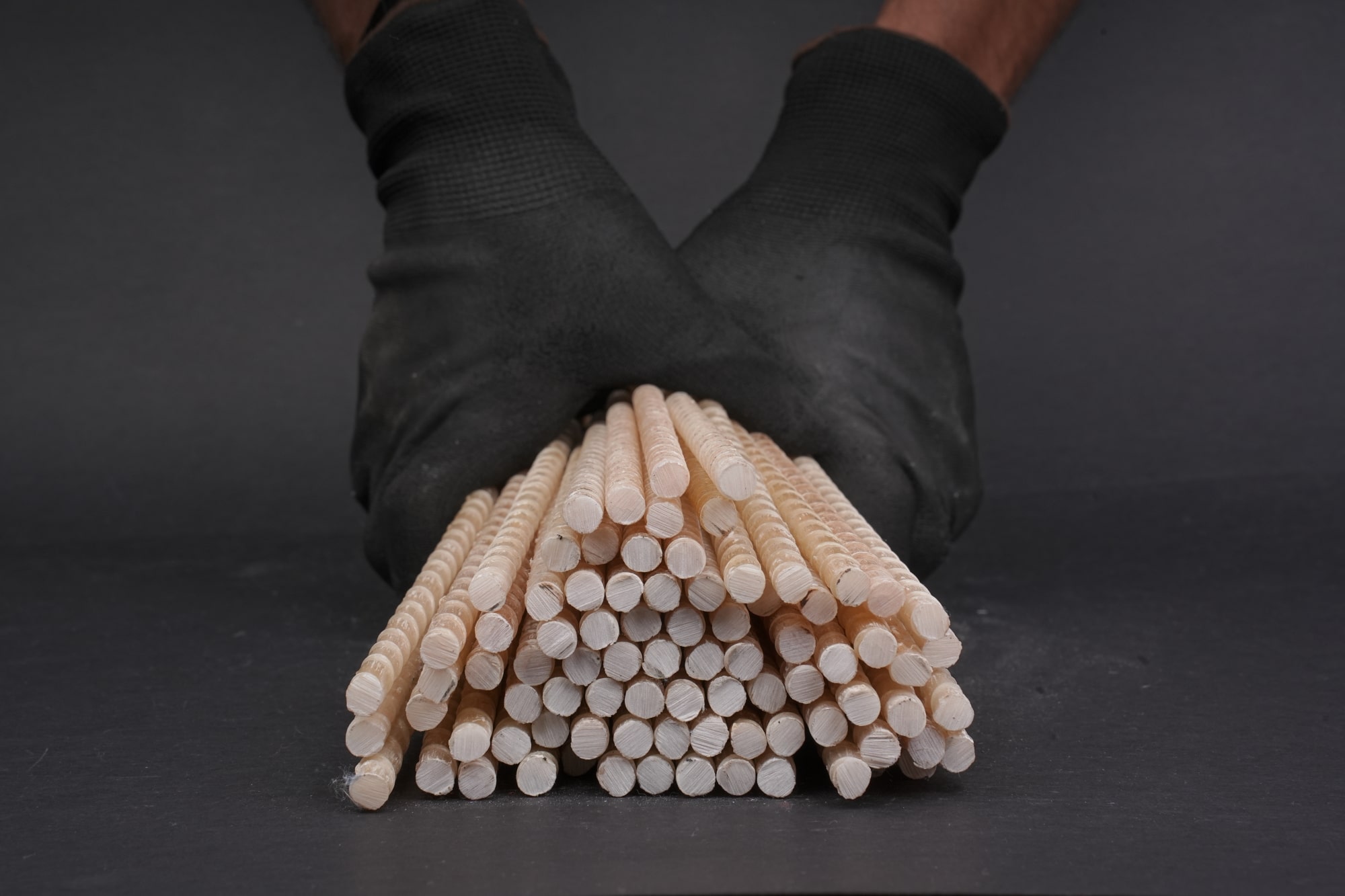

The Key Advantages of Using GFRP Rebar in Foundation Reinforcement

Corrosion Resistance
Unlike steel, GFRP rebar does not rust, making it ideal for foundation construction in harsh environments, such as coastal or industrial areas.

Lightweight
GFRP rebar is significantly lighter than steel. It simplifies the transportation and installation process, reducing labor costs and construction time.

Longevity
Foundations reinforced with GFRP rebar last longer, with lower maintenance needs. It provides better return on investment for construction projects.

High Strength
GFRP rebar provides excellent tensile strength. It helps improve the load-bearing capacity of a foundation. This is critical for both home building and large-scale infrastructure projects.
The Need for Foundations in Construction

Structural Stability
Foundations provide a firm base, ensuring that the building remains level and stable, even under varying loads or environmental conditions.
Load Distribution
They distribute the building’s weight to the ground, preventing stress concentration in specific areas, which could compromise structural integrity.

Moisture Resistance
Foundations act as a barrier against groundwater and soil moisture, protecting the building from dampness and water damage.

Durability
A well-constructed foundation safeguards the structure against shifting soil conditions, weather changes, and seismic activities.
Understanding Foundations
Essential Support for Structural Stability
A foundation is the lowest part of a building structure, responsible for transferring the load of the building to the ground. It ensures that the structure remains stable and level, preventing settlement or movement over time. Foundation construction plays a critical role in the overall safety and longevity of a building. The foundation’s design and material selection directly impact the durability and cost of the project. GFRP rebar, being a modern construction material, is now widely used in foundation construction to enhance strength and durability.
Strong Foundations
Building Confidence, Stability, and Longevity

Enhanced Safety
A strong foundation minimizes risks of structural failure, protecting the occupants and the building from accidents or natural calamities.

Cost-Effectiveness
Investing in a robust foundation reduces repairs or reconstruction in the future, saving time and money.

Resistance to Environmental Stress
Strong foundations can withstand environmental factors like soil erosion, flooding, or seismic activity, preserving the integrity of the building.

Longevity
Foundations built with durable materials like GFRP rebar ensure that the structure lasts longer with minimal maintenance requirements.

Versatility
A reliable foundation allows for diverse architectural designs and can support larger, more complex structures.

Improved Property Value
Buildings with durable and stable foundations are valued higher, making them a better investment for owners and buyers.
Exploring Foundation Types
Selecting the Best Fit for Your Project
Shallow Foundation
This type is typically used for small buildings like homes. Shallow foundations, such as slab-on-grade or mat foundations, are less expensive but require durable materials like GFRP rebar to prevent structural issues over time.

Deep Foundation
Used in larger construction projects where the load needs to be transferred to deeper, more stable soil layers. Examples include pile and caisson foundations, where GFRP rebar offers superior long-term performance, even in difficult ground conditions.
Strip Foundation
These are continuous strips of concrete that support load-bearing walls. GFRP rebar is often used in strip foundations to prevent corrosion and improve the longevity of the structure.

Raft Foundation
A large concrete slab that supports the entire structure, ideal for weak soils or heavy buildings. It evenly distributes loads, preventing settlement and reducing construction costs.
Contact Us
Get high performance GFRP composite rebar at the best price on your next project
Address
Office No 601, Twin Star South Block, Near Nanamava Circle, 150 Feet Ring Road Rajkot- 360004
- Testimonials